How Does an Ad Server Works?
Online advertising has evolved as and when the technology improved and publishers are enable to serve the interactive ads on their websites using the ad servers and other technologies. However, many people are not aware outside of Ad Ops on how does ad server works.
Here’s an article explaining what is an ad server to understand how does ad server works better. To understand the ad serving process easily, this article has been divided in to 3 sections as below.
To understand the process easily, the article has been divided in to 3 sections as below.
Calling Publisher Ad Tag: When the user opens the website (1), the publisher’s web server sends the ad request with all the possible user data to analyze i.e., (2) the ad request shares the browser where to get the content (3) and how format it on the website. A few HTML codes will return to the browser (4) includes a coded link called as ad tag. the ad tag redirects the browser to the publisher’s ad sever (5) to deliver the suitable ads on the ad slot.
Usually, the publisher ad server is a network of cloud servers owned and managed by ad server companies. In this scenario, the content server redirects the ad tag to fetch the ad from Google Ad Manager where the publisher has hosed the ads and run the ad selection process.
Ad Selection Process: In many scenarios, the ad servers run through the ad selection process to select the best possible ads to serve for the users based on the ad request received. The ad servers usually check for thousands of ads and its attributes to serve on the requested ad slot. The ad servers call the selected advertiser tag (6) to serve the ad as most of the time advertisers host their ads in their servers instead of hosting it in the publisher server. These redirects are technically called as 302 redirects and helps the ad servers to count the impression.
The only exception here is if the publisher decides to deliver house ad or the advertiser asked the publisher to site-serve ads. In both the cases, it requires publisher to load the actual ad into their ad server, it means that the publisher is a decider and ad request can skip the loop through advertiser side steps 7,8,11, and 12.
Calling Advertiser Ad Tag: The ad request calls the advertiser ad server (7) and redirected to fetch the actual ad hosted in Content Deliver Network or CDN (8). Ad Serving process usually redirect multiple times to fetch the selected ad, because of most of the time the front end ad servers are equipped to handle the number of ad requests from different ad servers at a same time. The CDNs will handle to load of hosting the creative and send it when there is request received from the ad server.
The CDNs are almost another company, like Akamai, that hosts the heavy creative files instead of hosting it in primary ad server. There are many CDN companies in the market, but Akamai has acquired most of the smaller companies and it is the largest player in this space.
In addition to sending back the ad request to CDN, the advertiser ad server also creates a second redirect (10) back to advertiser ad server to fetch the 1×1 pixel (11) once the ad is rendered. When the browser fires the final redirect calling 1×1 pixel from the advertiser’s ad server (11), the ad server records that the ad has rendered completely and it counts the impression.
In many scenarios, the bowser needs to make at least 4 redirects for the site served or house ads and six in case of third-party hosted ads for this whole process to work. However, the complete process will be completed in the seconds irrespective of how many redirects that ad servers do.
Here is the visual diagram process explained above steps – 302 redirects are highlighted in blue, and the ad creative is highlighted in red to understand better.
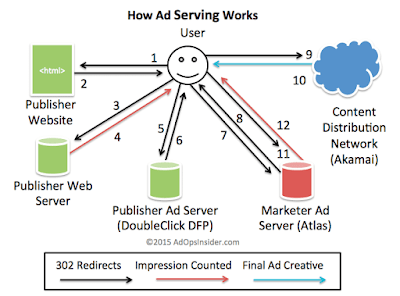
The below pictorial diagram helps understanding the ad serving process better. Please feel free to comment below with your questions to share the specific information that you are looking for with live examples.

Conclusion: The ad serving process is complex to understand the number of redirects to serve the ads. These redirects may create an issue in recording the impressions in both the publisher and advertiser ad servers accurately. It is always better to avoid unnecessary redirects while serving the ads and try to create an ad campaigns that select the best possible ads quickly instead of redirecting to multiple servers.




